Motion Correction in Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging
This is my final project for the Master in Computational Science and Engineering at EPFL. The goal here is to implement a post-processing algorithm to make true motion correction on cardiac MRI images. The anonymized dataset used for training and testing the model was provided by the CHUV. For confidentiality reasons, the repository is private and the methods will not be detailed here.
The project was divided into 2 main parts:
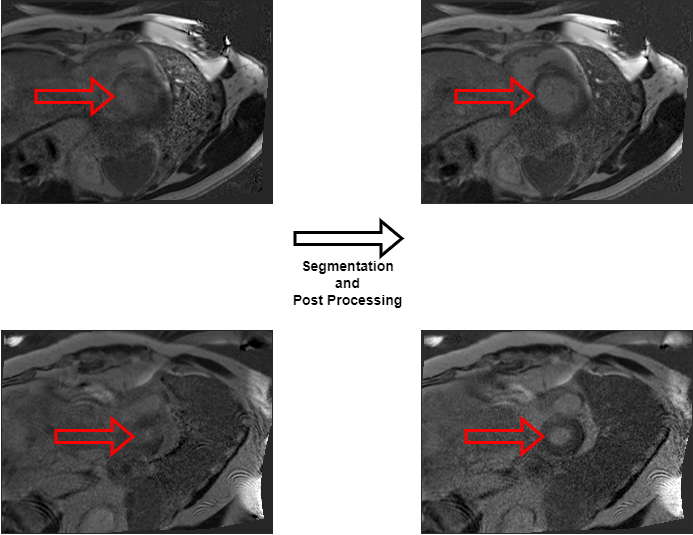
- Heart Segmentation: The first step was to segment the heart’s left ventricle out of the images. This was done using a U-Net architecture with a custom loss function. The model was trained on 200 images of size 204x272 pixels. The results were satisfactory, but due to the small siz of the dataset, the model was not able to generalize to new patients or to images coming from points to far away in the heart stack.
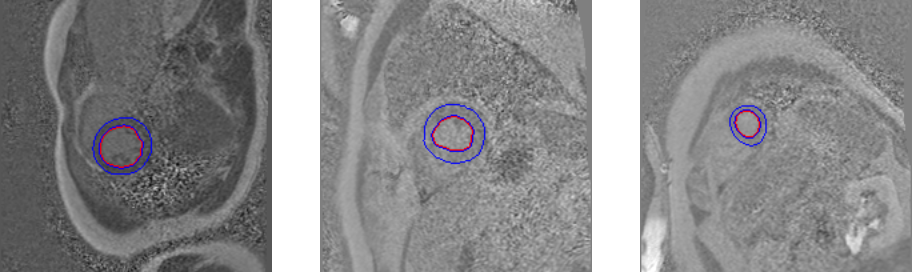
- Motion Correction: Using the segmentation made in the first step, we could extract some well selected features describing the left ventricle. These features were then used to improve the quality of the final scans by applying true-plane motion correction. This part of the project did not require any training of deep learning models.
By applying our motion correction algorithm, we could increase the quality of the final scans, reducing blurriness and removing ghosting on problematic scans. This can avoid the needs for repeated scans which are time-consuming and costly procedures but can also reduce the risk of misdiagnosis.